经典题型 链表 有序链表合并 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode (-1 ), p = dummy; ListNode p1 = l1, p2 = l2; while (p1 != null && p2 != null ) { if (p1.val > p2.val) { p.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; } else { p.next = p1; p1 = p1.next; } p = p.next; } if (p1 != null ) { p.next = p1; } if (p2 != null ) { p.next = p2; } return dummy.next; }
拓展:有序数组合并 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public int [] mergeTwoArrays(int [] arr1, int [] arr2) { int [] result = new int [arr1.length + arr2.length]; int i = 0 , j = 0 , k = 0 ; while (i < arr1.length && j < arr2.length) { if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) { result[k++] = arr1[i++]; } else { result[k++] = arr2[j++]; } } while (i < arr1.length) { result[k++] = arr1[i++]; } while (j < arr2.length) { result[k++] = arr2[j++]; } return result; }
拓展:有序数组逆序合并 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public int [] mergeTwoArraysInReverseOrder(int [] arr1, int [] arr2) { int [] result = new int [arr1.length + arr2.length]; int i = arr1.length - 1 , j = arr2.length - 1 , k = 0 ; while (i >= 0 && j >= 0 ) { if (arr1[i] >= arr2[j]) { result[k++] = arr1[i--]; } else { result[k++] = arr2[j--]; } } while (i >= 0 ) { result[k++] = arr1[i--]; } while (j >= 0 ) { result[k++] = arr2[j--]; } return result; }
重排链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public void reorderList (ListNode head) { Stack<ListNode> stk = new Stack <>(); ListNode p = head; while (p != null ) { stk.push(p); p = p.next; } p = head; while (p != null ) { ListNode lastNode = stk.pop(); ListNode next = p.next; if (lastNode == next || lastNode.next == next) { lastNode.next = null ; break ; } p.next = lastNode; lastNode.next = next; p = next; } } }
给定x分解单链表,使得小于x的数都在x之前 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 ListNode partition (ListNode head, int x) { ListNode dummy1 = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode dummy2 = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode p1 = dummy1, p2 = dummy2; ListNode p = head; while (p != null ) { if (p.val >= x) { p2.next = p; p2 = p2.next; } else { p1.next = p; p1 = p1.next; } ListNode temp = p.next; p.next = null ; p = temp; } p1.next = dummy2.next; return dummy1.next; }
返回链表的倒数第k个节点 快慢指针法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ListNode findFromEnd (ListNode head, int k) { ListNode p1 = head; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { p1 = p1.next; } ListNode p2 = head; while (p1 != null ) { p2 = p2.next; p1 = p1.next; } return p2; }
寻找链表的中间节点 快慢指针法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ListNode middleNode (ListNode head) { ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } return slow; }
判断链表是否包含环 快慢指针法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 boolean hasCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) { return true ; } } return false ; }
如果链表有环,找到环的入口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode fast, slow; fast = slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow) break ; } if (fast == null || fast.next == null ) { return null ; } slow = head; while (slow != fast) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; } }
相交链表 给定两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { ListNode p1 = headA, p2 = headB; while (p1 != p2) { if (p1 == null ) p1 = headB; else p1 = p1.next; if (p2 == null ) p2 = headA; else p2 = p2.next; } return p1; }
反转整个链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 public class ListNode { public int val; public ListNode next; public ListNode () {}; public ListNode (int val) { this .val = val; } public ListNode (int val, ListNode next) { this .val = val; this .next = next; } } ListNode reverse (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } ListNode last = reverse(head.next); head.next.next = head; head.next = null ; return last; } public static void printList (ListNode head) { ListNode current = head; while (current != null ) { System.out.print(current.val + " " ); current = current.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main (String[] args) { ListNode head = new ListNode (1 ); head.next = new ListNode (2 ); head.next.next = new ListNode (3 ); head.next.next.next = new ListNode (4 ); head.next.next.next.next = new ListNode (5 ); System.out.println("原始链表:" ); printList(head); ListNode reversedHead = reverse(head); System.out.println("反转后的链表:" ); printList(reversedHead); }
反转部分链表 递归法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 ListNode successor = null ; ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int m, int n) { if (m == 1 ) { return reverseN(head, n); } head.next = reverseBetween(head.next, m - 1 , n - 1 ); return head; } ListNode reverseN (ListNode head, int n) { if (n == 1 ) { successor = head.next; return head; } ListNode last = reverse(head.next, n - 1 ); head.next.next = head; head.next = successor; return last; }
k 个一组翻转链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) { if (head == null ) return null ; ListNode a, b; a = b = head; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { if (b == null ) return head; b = b.next; } ListNode newHead = reverse(a, b); a.next = reverseKGroup(b, k); return newHead; } ListNode reverse (ListNode a, ListNode b) { ListNode pre, cur, nxt; pre = null ; cur = a; nxt = a; while (cur != b) { nxt = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = nxt; } return pre; }
随机链表的复制 给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。构造这个链表的 深拷贝。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public Node copyRandomList (Node head) { HashMap<Node, Node> originToClone = new HashMap <>(); for (Node p = head; p != null ; p = p.next) { if (!originToClone.containsKey(p)) { originToClone.put(p, new Node (p.val)); } } for (Node p = head; p != null ; p = p.next) { if (p.next != null ) { originToClone.get(p).next = originToClone.get(p.next); } if (p.random != null ) { originToClone.get(p).random = originToClone.get(p.random); } } return originToClone.get(head); } }
有序链表删除重复元素(一个不留) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 public class RemoveDuplicates { static class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x) { val = x; } } public static ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) return null ; ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 ); dummy.next = head; ListNode prev = dummy; ListNode current = head; while (current != null ) { boolean isDuplicate = false ; while (current.next != null && current.val == current.next.val) { isDuplicate = true ; current = current.next; } if (isDuplicate) { prev.next = current.next; } else { prev = prev.next; } current = current.next; } return dummy.next; } public static void printList (ListNode head) { while (head != null ) { System.out.print(head.val + " " ); head = head.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int n = scanner.nextInt(); if (n == 0 ) { System.out.println(); return ; } ListNode head = new ListNode (scanner.nextInt()); ListNode current = head; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { current.next = new ListNode (scanner.nextInt()); current = current.next; } head = deleteDuplicates(head); printList(head); } }
数组 动态规划 爬楼梯 假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { int [] memo; public int climbStairs (int n) { memo = new int [n + 1 ]; return dp(n); } int dp (int n) { if (n <= 2 ) { return n; } if (memo[n] > 0 ) { return memo[n]; } memo[n] = dp(n - 1 ) + dp(n - 2 ); return memo[n]; } }
最大子数组和 给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; if (n == 0 ) return 0 ; int [] dp = new int [n]; dp[0 ] = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { dp[i] = Math.max(nums[i] + dp[i - 1 ], nums[i]); } int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { res = Math.max(res, dp[i]); } return res; }
最长递增子序列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, 1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (nums[j] < nums[i]) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1 ); } } } int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { res = Math.max(res, dp[i]); } return res; } }
编辑距离 给你两个单词 word1 和 word2, 请返回将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution { private int [][] memo; public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int m = word1.length(), n = word2.length(); memo = new int [m][n]; for (int [] row : memo) { Arrays.fill(row, -1 ); } return dp(word1, m - 1 , word2, n - 1 ); } private int dp (String s1, int i, String s2, int j) { if (i == -1 ) return j + 1 ; if (j == -1 ) return i + 1 ; if (memo[i][j] != -1 ) { return memo[i][j]; } if (s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(j)) { memo[i][j] = dp(s1, i - 1 , s2, j - 1 ); } else { memo[i][j] = min( dp(s1, i, s2, j - 1 ) + 1 , dp(s1, i - 1 , s2, j - 1 ) + 1 , dp(s1, i - 1 , s2, j) + 1 ); } return memo[i][j]; } private int min (int a, int b, int c) { return Math.min(Math.min(a, b), c); } }
最长回文子序列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int longestPalindromeSubseq (String s) { int n = s.length(); int [][] dp = new int [n][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { dp[i][i] = 1 ; } for (int i = n-2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { for (int j = i+1 ; j < n; j++) { if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) { dp[i][j] = dp[i+1 ][j-1 ] + 2 ; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1 ], dp[i+1 ][j]); } } } return dp[0 ][n-1 ]; } }
最长公共子序列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { private int [][] memo; public int longestCommonSubsequence (String text1, String text2) { memo = new int [text1.length()][text2.length()]; for (int [] row : memo) { Arrays.fill(row, -1 ); } return dp(text1, 0 , text2, 0 ); } private int dp (String s1, int i, String s2, int j) { if (i == s1.length() || j == s2.length()) return 0 ; if (memo[i][j] != -1 ) { return memo[i][j]; } if (s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(j)) { memo[i][j] = 1 + dp(s1, i+1 , s2, j+1 ); } else { memo[i][j] = Math.max(dp(s1, i+1 , s2, j), dp(s1, i, s2, j+1 )); } return memo[i][j]; } }
最长有效括号 给你一个只包含 ‘(‘ 和 ‘)’ 的字符串,找出最长有效(格式正确且连续)括号子串的长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public int longestValidParentheses (String s) { Stack<Integer> stk = new Stack <>(); int [] dp = new int [s.length() + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { if (s.charAt(i) == '(' ) { stk.push(i); dp[i + 1 ] = 0 ; } else { if (!stk.isEmpty()) { int leftIndex = stk.pop(); int len = 1 + i - leftIndex + dp[leftIndex]; dp[i + 1 ] = len; } else { dp[i + 1 ] = 0 ; } } } int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < dp.length; i++) { res = Math.max(res, dp[i]); } return res; } }
小于k的最大数 用指定的几个个位数(可重复)表示出小于n的最大整数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 import java.util.Arrays;public class MaxNumberLessThanN { public static int getLargest (int [] digits, int limit) { int result = -1 ; for (int digit : digits) { if (digit <= limit) { result = Math.max(result, digit); } } return result; } public static String findMax (int [] digits, String n) { char [] nArray = n.toCharArray(); int length = nArray.length; char [] result = new char [length]; boolean hasSmaller = false ; Arrays.sort(digits); for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { int limit = nArray[i] - '0' ; int largest = getLargest(digits, limit); if (largest == -1 ) { int j = i - 1 ; while (j >= 0 && result[j] == (char )(digits[0 ] + '0' )) { j--; } if (j < 0 ) { char [] newResult = new char [length - 1 ]; Arrays.fill(newResult, (char )(digits[digits.length - 1 ] + '0' )); return new String (newResult); } result[j] = (char )(getLargest(digits, result[j] - '0' - 1 ) + '0' ); for (int k = j + 1 ; k < length; k++) { result[k] = (char )(digits[digits.length - 1 ] + '0' ); } return new String (result); } result[i] = (char )(largest + '0' ); if (largest < limit) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < length; j++) { result[j] = (char )(digits[digits.length - 1 ] + '0' ); } return new String (result); } } return new String (result); } public static void main (String[] args) { int [] digits = {2 , 4 , 7 }; String n = "27221" ; String result = findMax(digits, n); System.out.println(result); } }
最长回文子串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public String palindrome (String s, int l, int r) { while (l >= 0 && r <= s.length() -1 && s.charAt(l) == s.charAt(r)) { l --; r ++; } return s.substring(l+1 , r); } public String longestPalindrome (String s) { String res = "" ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i ++) { String s1 = palindrome(s, i, i); String s2 = palindrome(s, i, i + 1 ); res = res.length() > s1.length() ? res : s1; res = res.length() > s2.length() ? res : s2; } return res; } }
滑动窗口 滑动窗口最大值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; int [] res = new int [n-k+1 ]; int resIndex = 0 ; PriorityQueue<int []> pq = new PriorityQueue <>(new Comparator <int []>() { public int compare (int [] a, int [] b) { return b[0 ] - a[0 ]; } }); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { pq.offer(new int []{nums[i], i}); while (pq.peek()[1 ] <= i - k) { pq.poll(); } if (i >= k - 1 ) { res[resIndex++] = pq.peek()[0 ]; } } return res; } }
无重复最长子串 给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长连续子字符串 的长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { int res = 0 ; HashMap<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap <>(); int left = 0 , right = 0 ; while (right < s.length()) { char c = s.charAt(right); right++; window.put(c, window.getOrDefault(c, 0 ) + 1 ); while (window.get(c) > 1 ) { char d = s.charAt(left); left++; window.put(d, window.get(d) - 1 ); } res = Math.max(right - left, res); } return res; } }
长度最小的子数组 给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 target。 找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ target 的长度最小的 连续子数组 [numsl, numsl+1, …, numsr-1, numsr] ,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int minSubArrayLen (int target, int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int left = 0 , right = 0 ; int sum = 0 ; while (right < n) { sum += nums[right]; while (sum >= target) { ans = Math.min(ans, right - left + 1 ); sum -= nums[left]; left++; } right++; } return ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : ans; } }
缓存淘汰策略 LRU缓存 LRU(Least Recently Used)策略是一种常见的缓存淘汰策略,它的核心思想是:如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高。LRU 算法的实现可以通过哈希表和双向链表来完成。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 class LRUCache { private int cap; private LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> cache; public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .cap = capacity; cache = new LinkedHashMap <>(); } public int get (int key) { if (!cache.containsKey(key)) return -1 ; makeNew(key); return cache.get(key); } public void put (int key, int value) { cache.put(key, value); makeNew(key); if (cache.size() > this .cap) { int head = cache.keySet().iterator().next(); cache.remove(head); } } private void makeNew (int key) { int value = cache.get(key); cache.remove(key); cache.put(key, value); } } public class LRUCache <K, V> extends LinkedHashMap <K, V> { private final int capacity; public LRUCache (int capacity) { super (capacity, 1f , true ); this .capacity = capacity; } @Override protected boolean removeEldestEntry (Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) { return size() > capacity; } public static void main (String[] args) { LRUCache<Integer, String> lruCache = new LRUCache <>(5 ); lruCache.put(1 , "apple" ); lruCache.put(2 , "banana" ); lruCache.put(3 , "pear" ); lruCache.put(4 , "watermelon" ); lruCache.put(5 , "peach" ); System.out.println(lruCache); lruCache.put(6 , "orange" ); System.out.println(lruCache); lruCache.get(4 ); System.out.println(lruCache); } }
LFU淘汰策略 LFU(Least Frequently Used)策略是根据数据使用的频率来决定淘汰哪一个数据的策略。使用频率最少的数据会被淘汰。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.LinkedHashSet;import java.util.Map;class LFUCache { private final int capacity; private int minFrequency; private final Map<Integer, Integer> valueMap; private final Map<Integer, Integer> frequencyMap; private final Map<Integer, LinkedHashSet<Integer>> frequencyListMap; public LFUCache (int capacity) { this .capacity = capacity; this .minFrequency = 0 ; this .valueMap = new HashMap <>(); this .frequencyMap = new HashMap <>(); this .frequencyListMap = new HashMap <>(); } public int get (int key) { if (!valueMap.containsKey(key)) { return -1 ; } int frequency = frequencyMap.get(key); frequencyMap.put(key, frequency + 1 ); frequencyListMap.get(frequency).remove(key); if (frequencyListMap.get(frequency).isEmpty()) { frequencyListMap.remove(frequency); if (frequency == minFrequency) { minFrequency++; } } frequencyListMap.computeIfAbsent(frequency + 1 , k -> new LinkedHashSet <>()).add(key); return valueMap.get(key); } public void put (int key, int value) { if (capacity <= 0 ) { return ; } if (valueMap.containsKey(key)) { valueMap.put(key, value); get(key); return ; } if (valueMap.size() >= capacity) { int evictKey = frequencyListMap.get(minFrequency).iterator().next(); frequencyListMap.get(minFrequency).remove(evictKey); if (frequencyListMap.get(minFrequency).isEmpty()) { frequencyListMap.remove(minFrequency); } valueMap.remove(evictKey); frequencyMap.remove(evictKey); } valueMap.put(key, value); frequencyMap.put(key, 1 ); minFrequency = 1 ; frequencyListMap.computeIfAbsent(1 , k -> new LinkedHashSet <>()).add(key); } }
FIFO淘汰策略 FIFO(First In First Out)策略是根据数据进入缓存的顺序来决定淘汰哪一个数据的策略。最早进入缓存的数据会被淘汰。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Queue;class FIFOCache { private final int capacity; private final Map<Integer, Integer> map; private final Queue<Integer> queue; public FIFOCache (int capacity) { this .capacity = capacity; this .map = new HashMap <>(); this .queue = new LinkedList <>(); } public int get (int key) { return map.getOrDefault(key, -1 ); } public void put (int key, int value) { if (map.containsKey(key)) { map.put(key, value); return ; } if (map.size() >= capacity) { int evictKey = queue.poll(); map.remove(evictKey); } map.put(key, value); queue.add(key); } }
排序算法
链接:https://learn.skyofit.com/archives/1291
复杂度
概念:
稳定:如果a原本在b前面且a=b,排序之后a仍然在b的前面。
不稳定:如果a原本在b的前面且a=b,排序之后 a 可能会出现在 b 的后面。
时间复杂度:对排序数据的总的操作次数。反映当n变化时,操作次数呈现什么规律。
空间复杂度:是指算法在计算机内执行时所需存储空间的度量,它也是数据规模n的函数。
In-Place:占用常数内存,不占用额外内存。比如:程序里没有创建新数组来保存数据,只用了临时变量。
Out-Place:占用额外内存。比如:创建了新的数组来保存或者处理数据。
冒泡排序 基本思想
算法描述
比较相邻的元素。如果前一个比后一个大,就交换它们两个;
对每一对相邻元素作同样的工作,从开始第一对到结尾的最后一对,这样在最后的元素应该会是最大的数;
针对所有的元素重复以上的步骤,除了最后一个;
重复步骤1~3,直到排序完成。为了优化算法,可以设立一个布尔标识,每趟排序开始前设为false,如果该趟排序发生了交换就置为true,如果一趟排序结束标识仍为false表示该趟排序没有发生交换,即数组已经有序,可以提前结束排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public static int [] bubbleSort(int [] array) { if (array.length == 0 ) return array; for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++){ boolean isSwap = false ; for (int j = 0 ; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (array[j + 1 ] < array[j]) { int temp = array[j + 1 ]; array[j + 1 ] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; isSwap = true ; } } if (!isSwap) break ; } return array; }
时间复杂度:冒泡排序平均时间复杂度为O(n2),最好时间复杂度为O(n),最坏时间复杂度为O(n2)。
最好情况:如果待排序元素本来是正序的,那么一趟冒泡排序就可以完成排序工作,比较和移动元素的次数分别是 (n – 1) 和 0,因此最好情况的时间复杂度为O(n)。
最坏情况:如果待排序元素本来是逆序的,需要进行 (n – 1) 趟排序,所需比较和移动次数分别为 n * (n – 1) / 2和 3 * n * (n-1) / 2。因此最坏情况下的时间复杂度为O(n2)。
空间复杂度:冒泡排序使用了常数空间,空间复杂度为O(1)
稳定性:当 array[j] == array[j+1] 的时候,不交换 array[i] 和 array[j],所以冒泡排序是稳定的。
拓展:鸡尾酒排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static void cocktailSort (int [] array) { int left = 0 ,right = array.length-1 ; while (left < right) { for (int i = left; i < right; i++) if (array[i] > array[i+1 ]) swap(array,i,i + 1 ); right--; for (int i = right; i > left; i--) if (array[i] < array[i-1 ]) swap(array,i,i-1 ); left++; } }
鸡尾酒排序是稳定的。它的平均时间复杂度为O(n2),最好情况是待排序列原先就是正序的,时间复杂度为O(n),最坏情况是待排序列原先是逆序的,时间复杂度为O(n2)。空间复杂度为O(1)。
选择排序 基本思想
算法描述
初始状态:无序区为R[1..n],有序区为空;
第i趟排序(i=1,2,3…n-1)开始时,当前有序区和无序区分别为R[1..i-1]和R[i..n]。该趟排序从当前无序区中选出关键字最小的记录 R[k],将它与无序区的第1个记录R交换,使R[1..i]和R[i+1..n]分别变为记录个数增加1个的新有序区和记录个数减少1个的新无序区;
(n-1)趟结束,数组有序化了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static int [] selectionSort(int [] array) { if (array.length == 0 ) return array; for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++) { int minIndex = i; for (int j = i; j < array.length; j++) { if (array[j] < array[minIndex]) minIndex = j; } int temp = array[minIndex]; array[minIndex] = array[i]; array[i] = temp; } return array; }
时间复杂度:简单选择排序平均时间复杂度为O(n2),最好时间复杂度为O(n2),最坏时间复杂度为O(n2)。
最好情况:如果待排序元素本来是正序的,则移动元素次数为 0,但需要进行 n * (n – 1) / 2 次比较。
最坏情况:如果待排序元素中第一个元素最大,其余元素从小到大排列,则仍然需要进行 n * (n – 1) / 2 次比较,且每趟排序都需要移动 3 次元素,即移动元素的次数为3 * (n – 1)次。
需要注意的是,简单选择排序过程中需要进行的比较次数与初始状态下待排序元素的排列情况无关。
空间复杂度:简单选择排序使用了常数空间,空间复杂度为O(1)
稳定性:简单选择排序不稳定,比如序列 2、4、2、1,知道第一趟排序第 1 个元素 2 会和 1 交换,那么原序列中 2 个 2 的相对前后顺序就被破坏了,所以简单选择排序不是一个稳定的排序算法。
直接插入排序 基本思想
算法描述
从第一个元素开始,该元素可以认为已经被排序;
取出下一个元素,在已经排序的元素序列中从后向前扫描;
如果该元素(已排序)大于新元素,将该元素移到下一位置;
重复步骤3,直到找到已排序的元素小于或者等于新元素的位置;
将新元素插入到该位置后;
重复步骤2~5。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static int [] insertionSort(int [] array) { if (array.length == 0 ) return array; int current; for (int i = 1 ; i < array.length; i++) { current = array[i]; int preIndex = i - 1 ; while (preIndex >= 0 && current < array[preIndex]) { array[preIndex + 1 ] = array[preIndex]; preIndex--; } array[preIndex + 1 ] = current; } return array; }
时间复杂度:直接插入排序平均时间复杂度为O(n2),最好时间复杂度为O(n),最坏时间复杂度为O(n2)。
最好情况:如果待排序元素本来是正序的,比较和移动元素的次数分别是 (n – 1) 和 0,因此最好情况的时间复杂度为O(n)。
最坏情况:如果待排序元素本来是逆序的,需要进行 (n – 1) 趟排序,所需比较和移动次数分别为 n * (n – 1) / 2和 n * (n – 1) / 2。因此最坏情况下的时间复杂度为O(n2)。
空间复杂度:直接插入排序使用了常数空间,空间复杂度为O(1)
稳定性:直接插入排序是稳定的。
拓展:在直接插入排序中,待插入的元素总是在有序区线性查找合适的插入位置,没有利用有序的优势,考虑使用二分查找搜索插入位置进行优化,即二分插入排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public static int [] BinaryInsertionSort(int [] array) { if (array.length == 0 ) return array; for (int i = 1 ;i < array.length;i++) { int left = 0 ; int right = i - 1 ; int current = array[i]; while (left <= right) { int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1 ); if (array[mid] > current){ right = mid - 1 ; }else { left = mid + 1 ; } } for (int j = i - 1 ;j >= left;j--) { array[j + 1 ] = array[j]; } array[left] = current; } return array; }
二分插入排序是稳定的。它的平均时间复杂度是O(n2),最好时间复杂度为O(nlogn),最坏时间复杂度为O(n2)。
希尔排序 基本思想
算法描述
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static int [] ShellSort(int [] array) { int len = array.length; if (len == 0 ) return array; int current, gap = len / 2 ; while (gap > 0 ) { for (int i = gap; i < len; i++) { current = array[i]; int preIndex = i - gap; while (preIndex >= 0 && array[preIndex] > current) { array[preIndex + gap] = array[preIndex]; preIndex -= gap; } array[preIndex + gap] = current; } gap /= 2 ; } return array; }
时间复杂度:希尔排序平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn),最好时间复杂度为O(nlog2n),最坏时间复杂度为O(nlog2n)。希尔排序的时间复杂度与增量序列的选取有关。
空间复杂度:希尔排序使用了常数空间,空间复杂度为O(1)
稳定性:由于相同的元素可能在各自的序列中插入排序,最后其稳定性就会被打乱,比如序列 2、4、1、2,所以希尔排序是不稳定的。
归并排序 基本思想
算法描述
把长度为 n 的输入序列分成两个长度为 n / 2 的子序列;
对这两个子序列分别采用归并排序;
将两个排序好的子序列合并成一个最终的排序序列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public static int [] MergeSort(int [] array) { if (array.length < 2 ) return array; int mid = array.length / 2 ; int [] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, 0 , mid); int [] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, mid, array.length); return merge(MergeSort(left), MergeSort(right)); } public static int [] merge(int [] left, int [] right) { int [] result = new int [left.length + right.length]; int i = 0 ,j = 0 ,k = 0 ; while (i < left.length && j < right.length) { if (left[i] <= right[j]) { result[k++] = left[i++]; } else { result[k++] = right[j++]; } } while (i < left.length) { result[k++] = left[i++]; } while (j < right.length) { result[k++] = right[j++]; } return result; }
时间复杂度:归并排序平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn),最好时间复杂度为O(nlogn),最坏时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。归并排序的形式就是一棵二叉树,它需要遍历的次数就是二叉树的深度,而根据完全二叉树的可以得出它在任何情况下时间复杂度均是O(nlogn)。
空间复杂度:归并排序空间复杂度为O(n)
稳定性:归并排序是稳定的。
快速排序 基本思想
算法描述
从数列中挑出一个元素,称为 “基准”(pivot);
重新排序数列,所有比基准值小的元素放在基准前面,所有比基准值大的元素放在基准的后面(相同的数可以到任一边),该基准就处于数列的中间位置。这称为分区(partition)操作;
递归地(recursive)对小于基准值元素的子数列和大于基准值元素的子数列进行快速排序。
代码实现
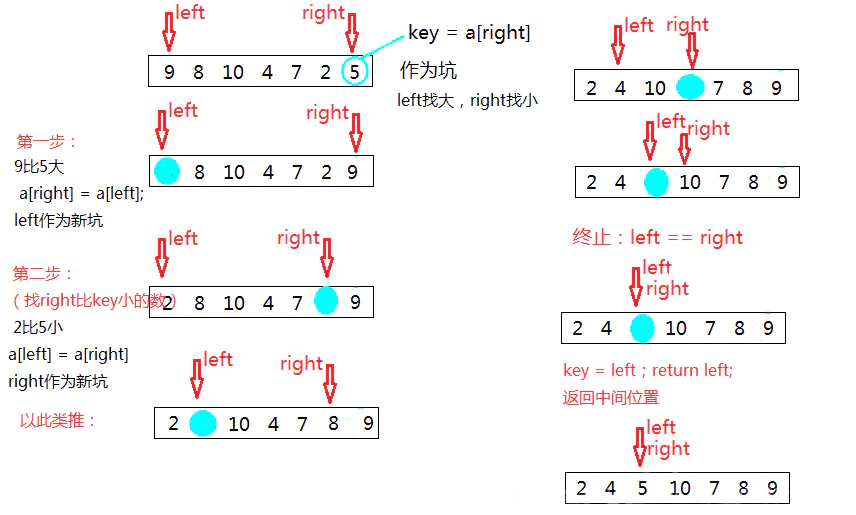
两种方法:左右指针法、挖坑法
将数组的最后一个数 right 作为基准数 key。
分区过程:从数组的首元素 begin 开始向后找比 key 大的数(begin 找大);end 开始向前找比 key 小的数(end 找小);找到后交换两者(swap),直到 begin >= end 终止遍历。最后将 begin(此时begin == end)和最后一个数交换( 这个时候 end 不是最后一个位置),即 key 作为中间数(左区间都是比key小的数,右区间都是比key大的数)
再对左右区间重复第二步,直到各区间只有一个数。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class Demo { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] a = {3 , 5 , 8 , 1 , 2 , 9 , 4 , 7 , 6 }; sort(a, 0 , a.length - 1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++){ System.out.print(a[i] + "," ); } } public static void sort (int [] array,int left,int right) { int p = left; int q = right; int key = right; if (left >= right) return ; while ( p < q ) { while (p < q && array[p] <= array[key]) p++; while (p < q && array[q] >= array[key]) q--; if (p < q) swap(array, p, q); } swap(array, p, key); sort(array, left, p - 1 ); sort(array, q + 1 , right); } public static void swap (int [] array, int i, int j) { int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; } }
定义两个指针 left 指向起始位置,right 指向最后一个元素的位置,然后指定一个基准 key(right),作为坑。
left 寻找比基准(key)大的数字,找到后将 left 的数据赋给 right,left 成为一个坑,然后 right 寻找比基数(key)小的数字,找到将 right 的数据赋给 left,right 成为一个新坑,循环这个过程,直到 begin 指针与 end指针相遇,然后将 key 填入那个坑(最终:key的左边都是比key小的数,key的右边都是比key大的数),然后进行递归操作。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public static void Quicksort (int array[], int left, int right) { if (left < right){ int pos = partition(array, left, right); Quicksort(array, left, pos - 1 ); Quicksort(array, pos + 1 , right); } } public static int partition (int [] array,int left,int right) { int key = array[right]; while (left < right) { while (left < right && array[left] <= key ) left++; array[right] = array[left]; while (left <right && array[right] >= key) right--; array[left] = array[right]; } array[left] = key; return left; }
优化 之前选择基准的策略都是固定基准,即固定地选择序列的右边界值作为基准,但如果在待排序列几乎有序的情况下,选择的固定基准将是序列的最大(小)值,快排的性能不好(因为每趟排序后,左右两个子序列规模相差悬殊,大的那部分最后时间复杂度很可能会达到O(n2))。
优化一:随机基准
1 2 3 4 int random = (int ) (left + Math.random() * (right - left + 1 ));swap(array, random, right);
优化二:三数取中法
举个例子,对于int[] array = { 2,5,4,9,3,6,8,7,1,0},2、3、0分别是第一个数,第(N/2)个是数以及最后一个数,三个数中3最大,0最小,2在中间,所以取2为基准值。
实现getMid函数即可:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static int getMid (int [] array,int left,int right) { int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1 ); int a = array[left]; int b = array[mid]; int c = array[right]; if ((b <= a && a <= c) || (c <= a && a <= b)) { return left; } if ((a <= b && b <= c) || (c <= b && b <= a)) { return mid; } if ((a <= c && c <= b) || (b <= c && c <= a)) { return right; } return left; }
优化三:当待排序序列的长度分割到一定大小后,使用插入排序
实现方式也很简单,快排是在子序列元素个数为 1 时才停止递归,可以设置一个阈值n,假设为5,则大于5个元素,子序列继续递归,否则选用插排。
此时QuickSort()函数如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public static void Quicksort (int array[], int left, int right) { if (right - left > 5 ){ int pos = partition(array, left, right); Quicksort(array, left, pos - 1 ); Quicksort(array, pos + 1 , right); }else { insertionSort(array); } }
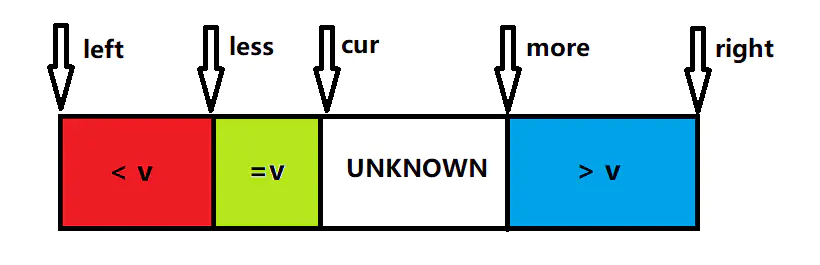
优化四:三路划分
三路划分的思想是利用 partition 函数将待排序列划分为三部分:第一部分小于基准v,第二部分等于基准v,第三部分大于基准v。这样在递归排序区间的时候,就不必再对第二部分元素均相等的区间进行快排了,这在待排序列存在大量相同元素的情况下能大大提高快排效率。
红色部分为小于基准v的序列,绿色部分为等于基准v的序列,白色部分由于还未被 cur 指针遍历到,属于大小未知的部分,蓝色部分为大于基准v的序列。
left 指针为整个待排区间的左边界,right 指针为整个待排区间的右边界。less 指针指向红色部分的最后一个数(即小于v的最右位置),more 指针指向蓝色部分的第一个数(即大于v的最左位置)。cur 指针指向白色部分(未知部分)的第一个数,即下一个要判断大小的位置。
算法思路:
由于最初红色和蓝色区域没有元素,初始化 less = left – 1,more = right + 1,cur = left。整个区间为未知部分(白色)。
如果当前 array[cur] < v,则 swap(array,++less,cur++),即把红色区域向右扩大一格(less指针后移),把 array[cur] 交换到该位置,cur 指针前移判断下一个数。
如果当前 array[cur] = v,则不必交换,直接 cur++
如果当前 array[cur] > v,则 swap(array,–more,cur),即把蓝色区域向左扩大一格(more指针前移),把 array[cur] 交换到该位置。特别注意!此时cur指针不能前移,这是因为交换到cur位置的元素来自未知区域,还需要进一步判断array[cur]。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public static int [] partition(int [] array,int left,int right){ int v = array[right]; int less = left - 1 ; int more = right + 1 ; int cur = left; while (cur < more){ if (array[cur] < v){ swap(array,++less,cur++); }else if (array[cur] > v){ swap(array,--more,cur); }else { cur++; } } return new int []{less + 1 ,more - 1 }; } public static void swap (int [] array, int i, int j) { int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; } public static void Quicksort (int array[], int left, int right) { if (left < right) { int [] p = partition(array,left,right); Quicksort(array,left,p[0 ] - 1 ); Quicksort(array,p[1 ] + 1 ,right); } }
时间复杂度:快速排序平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn),最好时间复杂度为O(nlogn),最坏时间复杂度为O(n2)。
最好情况:基准选择得当,partition函数每次恰好能均分序列,其递归树的深度就为logn,时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。
最坏情况:选择了最大或者最小数字作为基准,每次划分只能将序列分为一个元素与其他元素两部分,此时快速排序退化为冒泡排序,如果用树画出来,得到的将会是一棵单斜树,即所有的结点只有左(右)结点的树,树的深度为 n,时间复杂度为O(n2)。
空间复杂度:快速排序的空间复杂度主要考虑递归时使用的栈空间。在最好情况下,即partition函数每次恰好能均分序列,空间复杂度为O(logn);在最坏情况下,即退化为冒泡排序,空间复杂度为O(n)。平均空间复杂度为O(logn)。
稳定性:快速排序是不稳定的。
堆排序 基本思想
算法描述
将初始待排序关键字序列(R1,R2….Rn)构建成大顶堆,此堆为初始的无序区;
将堆顶元素R[1]与最后一个元素R[n]交换,此时得到新的无序区(R1,R2,……Rn-1)和新的有序区(Rn),且满足R[1,2…n-1]<=R[n];
由于交换后新的堆顶R[1]可能违反堆的性质,因此需要对当前无序区(R1,R2,……Rn-1)调整为新堆,然后再次将R[1]与无序区最后一个元素交换,得到新的无序区(R1,R2….Rn-2)和新的有序区(Rn-1,Rn)。不断重复此过程直到有序区的元素个数为(n-1),则整个排序过程完成。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 static int len;public static int [] HeapSort(int [] array) { len = array.length; if (len == 0 ) return array; buildMaxHeap(array); while (len > 0 ) { swap(array, 0 , len - 1 ); len--; adjustHeap(array, 0 ); } return array; } public static void adjustHeap (int [] array, int i) { int maxIndex = i; if (2 * i + 1 < len && array[2 * i + 1 ] > array[maxIndex]) maxIndex = 2 * i + 1 ; if (2 * i + 2 < len && array[2 * i + 2 ] > array[maxIndex]) maxIndex = 2 * i + 2 ; if (maxIndex != i) { swap(array, maxIndex, i); adjustHeap(array, maxIndex); } } public static void buildMaxHeap (int [] array) { for (int i = (len - 2 ) / 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { adjustHeap(array, i); } } public static void swap (int [] array, int i, int j) { int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; }
拓展:
插入元素:只需要把待插入的元素放置在堆尾,然后 len++ 把其纳入堆,然后调用 adjustHeap 函数重新调整堆即可。
删除堆顶元素:只需要把堆顶元素交换到堆尾,然后 len– 把其移出堆,然后调用 adjustHeap 函数重新调整堆即可。
时间复杂度:堆排序平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn),最好时间复杂度为O(nlogn),最坏时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。堆排序的形式就是一棵二叉树,它需要遍历的次数就是二叉树的深度,而根据完全二叉树的可以得出它在任何情况下时间复杂度均是O(nlogn)。
空间复杂度:堆排序使用了常数空间,空间复杂度为O(1)。
稳定性:堆排序是不稳定的。
计数排序 基本思想
算法描述
找出待排序的数组中最大和最小的元素;
统计数组中每个值为 i 的元素出现的次数,存入数组C的第i项;
对所有的计数累加(从C中的第一个元素开始,每一项和前一项相加);
反向填充目标数组:将每个元素 i 放在新数组的第C(i)项,每放一个元素就将C(i)减去1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public static int [] CountingSort(int [] array) { if (array.length == 0 ) return array; int bias, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++) { max = Math.max(max, array[i]); min = Math.min(min, array[i]); } bias = -min; int [] bucket = new int [max - min + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(bucket, 0 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++) { bucket[array[i] + bias]++; } int index = 0 , i = 0 ; while (index < array.length) { if (bucket[i] != 0 ) { array[index] = i - bias; bucket[i]--; index++; } else i++; } return array; }
时间复杂度:计数排序平均时间复杂度为O(n + k),最好时间复杂度为O(n + k),最坏时间复杂度为O(n + k)。n 为遍历一趟数组计数过程的复杂度,k 为遍历一趟桶取出元素过程的复杂度。
空间复杂度:计数排序空间复杂度为O(k),k为桶数组的长度。
稳定性:计数排序是稳定的。
桶排序 基本思想
算法描述
设置一个定量的数组当作空桶;
遍历输入数据,并且把数据一个一个放到对应的桶里去;
对每个不是空的桶的桶内元素进行排序(可以使用直接插入排序等);
从不是空的桶里把排好序的数据拼接起来。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public static int [] bucketSort(int [] array){ int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++){ max = Math.max(max, array[i]); min = Math.min(min, array[i]); } int bucketNum = (max - min) / array.length + 1 ; ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> bucketArr = new ArrayList <>(bucketNum); for (int i = 0 ; i < bucketNum; i++){ bucketArr.add(new ArrayList <Integer>()); } for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++){ int num = (array[i] - min) / (array.length); bucketArr.get(num).add(array[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < bucketArr.size(); i++){ Collections.sort(bucketArr.get(i)); } int k = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < bucketArr.size(); i++){ for (int j = 0 ;j < bucketArr.get(i).size();j++) { array[k++] = bucketArr.get(i).get(j); } } return array; }
时间复杂度:桶排序平均时间复杂度为O(n + k),最好时间复杂度为O(n + k),最坏时间复杂度为O(n2)。
空间复杂度:桶排序空间复杂度为O(n + k)。
稳定性:桶排序是稳定的。
基数排序 基本思想
算法描述
取得数组中的最大数,并取得位数;
array 为原始数组,从最低位开始取每个位组成 radix 数组;
对 radix 进行计数排序(利用计数排序适用于小范围数的特点);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public static int [] RadixSort(int [] array) { if (array == null || array.length < 2 ) return array; int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++) { max = Math.max(max, array[i]); } int maxDigit = 0 ; while (max != 0 ) { max /= 10 ; maxDigit++; } int div = 1 ; ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> bucketList = new ArrayList <ArrayList<Integer>>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) bucketList.add(new ArrayList <Integer>()); for (int i = 0 ; i < maxDigit; i++,div *= 10 ) { for (int j = 0 ; j < array.length; j++) { int num = (array[j] / div) % 10 ; bucketList.get(num).add(array[j]); } int index = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < bucketList.size(); j++) { for (int k = 0 ; k < bucketList.get(j).size(); k++) array[index++] = bucketList.get(j).get(k); bucketList.get(j).clear(); } } return array; }
时间复杂度:基数排序平均时间复杂度为O(n * k),最好时间复杂度为O(n * k),最坏时间复杂度为O(n * k)。
空间复杂度:基数排序空间复杂度为O(n + k)。
稳定性:基数排序是稳定的。
二分查找 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public class BinarySearch { public static int binarySearch(int[] array, int target) { int left = 0; int right = array.length - 1; while (left <= right) { int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; // 防止整形的(left + right)/2溢出 if (array[mid] == target) { return mid; } else if (array[mid] < target) { left = mid + 1; } else { right = mid - 1; } } return -1; // 未找到目标值 } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13}; int target = 7; int result = binarySearch(array, target); System.out.println("目标值的索引: " + result); } } // 递归实现 public class BinarySearch { public static int binarySearch(int[] array, int target, int left, int right) { if (left > right) { return -1; } int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; if (array[mid] == target) { return mid; } else if (array[mid] < target) { return binarySearch(array, target, mid + 1, right); } else { return binarySearch(array, target, left, mid - 1); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13}; int target = 7; int result = binarySearch(array, target, 0, array.length - 1); System.out.println("目标值的索引: " + result); } }
寻找左右边界的二分查找 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 int binary_search (int [] nums, int target) { int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] < target) { left = mid + 1 ; } else if (nums[mid] > target) { right = mid - 1 ; } else if (nums[mid] == target) { return mid; } } return -1 ; } private int left_bound (int [] nums, int target) { int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] == target) { right = mid - 1 ; } else if (nums[mid] < target) { left = mid + 1 ; } else if (nums[mid] > target) { right = mid - 1 ; } } if (left < 0 || left >= nums.length) { return -1 ; } return nums[left] == target ? left : -1 ; } private int right_bound (int [] nums, int target) { int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] == target) { left = mid + 1 ; } else if (nums[mid] < target) { left = mid + 1 ; } else if (nums[mid] > target) { right = mid - 1 ; } } if (right < 0 || right >= nums.length) { return -1 ; } return nums[right] == target ? right : -1 ; }
递归删除文件夹 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import java.io.File;public class FileDeleter { public static void main (String[] args) { String path = "example" ; boolean result = deleteRecursively(new File (path)); if (result) { System.out.println("删除成功: " + path); } else { System.out.println("删除失败: " + path); } } public static boolean deleteRecursively (File file) { if (!file.exists()) { System.out.println("文件不存在: " + file.getAbsolutePath()); return false ; } if (file.isDirectory()) { File[] files = file.listFiles(); if (files != null ) { for (File child : files) { if (!deleteRecursively(child)) { return false ; } } } } return file.delete(); } }
两数之和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { int n = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; ++j) { if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) { return new int []{i, j}; } } } return new int [0 ]; } }
三数之和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { private List<List<Integer>> towSum (int [] nums, int start, int target) { int low = start, high = nums.length - 1 ; List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); while (low < high) { int sum = nums[low] + nums[high]; int left = nums[low], right = nums[high]; if (sum < target) { while (low < high && nums[low] == left) low++; } else if (sum > target) { while (low < high && nums[high] == right) high--; } else { res.add(new ArrayList <>(Arrays.asList(left, right))); while (low < high && nums[low] == left) low++; while (low < high && nums[high] == right) high--; } } return res; } public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums, int target) { int n = nums.length; Arrays.sort(nums); List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { List<List<Integer>> twoSumRes = towSum(nums, i+1 , target -nums[i]); for (List<Integer> tuple : twoSumRes) { tuple.add(nums[i]); res.add(tuple); } while (i < n-1 && nums[i] == nums[i+1 ]) i++; } return res; } }
最接近的三数之和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int ClosestSum (int [] nums, int target) { int n = nums.length; Arrays.sort(nums); int delta = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 2 ; i++) { int sum = nums[i] + ClosestSum2(nums, i + 1 , target - nums[i]); if (Math.abs(delta) > Math.abs(target - sum)) { delta = target - sum; if (delta == 0 ) { break ; } } } return target - delta; } private int ClosestSum2 (int [] nums, int start, int target) { int low = start; int high = nums.length - 1 ; int delta = Integer.MAX_VALUE; while (low < high) { int sum = nums[low] + nums[high]; if (Math.abs(delta) > Math.abs(target - sum)) { delta = target - sum; if (delta == 0 ) { break ; } } if (sum < target) { low++; } else { high--; } } return target - delta; } }
接雨水 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int n = height.length; if (n == 0 ) return 0 ; int res = 0 ; int [] l_max = new int [n]; int [] r_max = new int [n]; l_max[0 ] = height[0 ]; r_max[n-1 ] = height[n-1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { l_max[i] = Math.max(height[i], l_max[i-1 ]); } for (int i = n-2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { r_max[i] = Math.max(height[i], r_max[i+1 ]); } for (int i = 1 ; i < n-1 ; i++) { res += Math.min(l_max[i], r_max[i]) - height[i]; } return res; } } class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int n = height.length; if (n == 0 ) return 0 ; int res = 0 ; int left = 0 , right = height.length - 1 ; int l_max = 0 , r_max = 0 ; while (left < right) { l_max = Math.max(l_max, height[left]); r_max = Math.max(r_max, height[right]); if (l_max < r_max) { res += l_max - height[left]; left++; } else { res += r_max - height[right]; right--; } } return res; } }
字符串解码 给定一个经过编码的字符串,返回它解码后的字符串。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import java.util.*;class Solution { public String decodeString (String s) { StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder (); Stack<Integer> multi_stack = new Stack <>(); Stack<String> res_stack = new Stack <>(); int multi = 0 ; for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { if (c >= '0' && c<= '9' ) { multi = multi * 10 + Integer.parseInt(c + "" ); } else if (c == '[' ) { multi_stack.push(multi); res_stack.push(res.toString()); multi = 0 ; res = new StringBuilder (); } else if (c == ']' ) { StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder (); int cur_multi = multi_stack.peek(); multi_stack.pop(); String last_res = res_stack.peek(); res_stack.pop(); for (int i = 0 ; i < cur_multi; i++) { temp.append(res); } res = new StringBuilder (last_res + temp); } else { res.append(c); } } return res.toString(); } }
每日温度 给定一个整数数组 temperatures ,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指对于第 i 天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) { int n = temperatures.length; int [] res = new int [n]; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); for (int i = n-1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] >= temperatures[stack.peek()]) { stack.pop(); } res[i] = stack.isEmpty() ? 0 : (stack.peek() - i); stack.push(i); } return res; } }
下一个更大的元素1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution { public int [] nextGreaterElement(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int [] greater = calculateGreaterElement(nums2); HashMap<Integer, Integer> greaterMap = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums2.length; i++) { greaterMap.put(nums2[i], greater[i]); } int [] res = new int [nums1.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums1.length; i++) { res[i] = greaterMap.get(nums1[i]); } return res; } int [] calculateGreaterElement(int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int [] res = new int [n]; Stack<Integer> s = new Stack <>(); for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { while (!s.isEmpty() && s.peek() <= nums[i]) { s.pop(); } res[i] = s.isEmpty() ? -1 : s.peek(); s.push(nums[i]); } return res; } }
下一个更大的元素2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int [] calculateGreaterElement(int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int [] res = new int [n]; Stack<Integer> s = new Stack <>(); for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { while (!s.isEmpty() && s.peek() <= nums[i]) { s.pop(); } res[i] = s.isEmpty() ? -1 : s.peek(); s.push(nums[i]); } return res; }
判断是否是质数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution { public boolean isPrime (int n) { if (n < 2 ) return false ; for (int i = 2 ; i * i <= n; i++) { if (n % i == 0 ) return false ; } return true ; } }
ArrayList实现最大堆 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 import java.util.ArrayList;public class MaxHeap { private ArrayList<Integer> heap; public MaxHeap () { heap = new ArrayList <>(); } public void insert (int value) { heap.add(value); heapifyUp(heap.size() - 1 ); } public int extractMax () { if (heap.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Heap is empty" ); } int max = heap.get(0 ); int last = heap.remove(heap.size() - 1 ); if (!heap.isEmpty()) { heap.set(0 , last); heapifyDown(0 ); } return max; } private void heapifyUp (int index) { while (index > 0 ) { int parentIndex = (index - 1 ) / 2 ; if (heap.get(index) > heap.get(parentIndex)) { swap(index, parentIndex); index = parentIndex; } else { break ; } } } private void heapifyDown (int index) { int size = heap.size(); while (index < size) { int leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1 ; int rightChildIndex = 2 * index + 2 ; int largestIndex = index; if (leftChildIndex < size && heap.get(leftChildIndex) > heap.get(largestIndex)) { largestIndex = leftChildIndex; } if (rightChildIndex < size && heap.get(rightChildIndex) > heap.get(largestIndex)) { largestIndex = rightChildIndex; } if (largestIndex != index) { swap(index, largestIndex); index = largestIndex; } else { break ; } } } private void swap (int index1, int index2) { int temp = heap.get(index1); heap.set(index1, heap.get(index2)); heap.set(index2, temp); } public static void main (String[] args) { MaxHeap maxHeap = new MaxHeap (); maxHeap.insert(10 ); maxHeap.insert(20 ); maxHeap.insert(5 ); System.out.println("Max element: " + maxHeap.extractMax()); System.out.println("Max element: " + maxHeap.extractMax()); System.out.println("Max element: " + maxHeap.extractMax()); } }
最长有效括号 保持栈底元素为当前已经遍历过的元素中「最后一个没有被匹配的右括号的下标」,这样的做法主要是考虑了边界条件的处理,栈里其他元素维护左括号的下标:
对于遇到的每个 ‘(’ ,将它的下标放入栈中
对于遇到的每个 ‘)’ ,先弹出栈顶元素表示匹配了当前右括号:
如果栈为空,说明当前的右括号为没有被匹配的右括号,将其下标放入栈中来更新我们之前提到的「最后一个没有被匹配的右括号的下标」
如果栈不为空,当前右括号的下标减去栈顶元素即为「以该右括号为结尾的最长有效括号的长度」1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int longestValidParentheses (String s) { int maxans = 0 ; Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList <Integer>(); stack.push(-1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { if (s.charAt(i) == '(' ) { stack.push(i); } else { stack.pop(); if (stack.isEmpty()) { stack.push(i); } else { maxans = Math.max(maxans, i - stack.peek()); } } } return maxans; } }
判断是否是回文串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 private static boolean isPalindrome (String s) { for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length()/2 ; i++) { if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(s.length()-1 -i)) { return false ; } } return true ; }
最大公约数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class GCD { public static int gcdRecursive (int a, int b) { if (b == 0 ) { return a; } return gcdRecursive(b, a % b); } public static int gcdIterative (int a, int b) { while (b != 0 ) { int temp = b; b = a % b; a = temp; } return a; } }
创建三个线程有序打印1-100 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public class ConcurrentDemo { private static final int MAX_NUMBER = 100 ; private static int number = 1 ; private static final Object lock = new Object (); public static void main (String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread (new PrintTask (1 )); Thread t2 = new Thread (new PrintTask (2 )); Thread t3 = new Thread (new PrintTask (0 )); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } static class PrintTask implements Runnable { private int threadId; public PrintTask (int threadId) { this .threadId = threadId; } @Override public void run () { while (true ) { synchronized (lock) { while (number % 3 != threadId) { try { lock.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } if (number > MAX_NUMBER) { lock.notifyAll(); break ; } System.out.println("Thread-" + threadId + " prints: " + number++); lock.notifyAll(); } } } } }
SQL模拟死锁 为了展示如何在事务中引发死锁,可以创建一个简单的数据库表,然后编写两个事务,在特定的情况下导致死锁。下面以MySQL为例,假设有一张users表,事务1和事务2分别对不同的记录进行锁定,但由于它们相互等待对方释放锁而产生了死锁。
创建表结构
1 2 3 4 5 CREATE TABLE users ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR (100 ), balance DECIMAL (10 , 2 ) );
插入一些初始数据
1 2 INSERT INTO users (id, name, balance) VALUES (1 , 'Alice' , 100.00 );INSERT INTO users (id, name, balance) VALUES (2 , 'Bob' , 200.00 );
模拟死锁的两个事务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 START TRANSACTION;UPDATE users SET balance = balance - 50 WHERE id = 1 ;DO SLEEP(5 ); UPDATE users SET balance = balance + 50 WHERE id = 2 ;COMMIT ;START TRANSACTION;UPDATE users SET balance = balance + 50 WHERE id = 2 ;DO SLEEP(5 ); UPDATE users SET balance = balance - 50 WHERE id = 1 ;COMMIT ;
事务1 先更新用户1的记录,此时用户1的记录被事务1锁定。事务2 先更新用户2的记录,此时用户2的记录被事务2锁定。事务1 尝试更新用户2的记录,但用户2的记录已被事务2锁定,所以事务1进入等待状态。事务2 尝试更新用户1的记录,但用户1的记录已被事务1锁定,所以事务2也进入等待状态。
由于两个事务互相等待对方释放锁,导致了死锁。最终数据库检测到死锁后,会主动回滚其中一个事务,以解除死锁。
模拟死锁 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class DeadLockSample { private final Object lock1 = new Object (); private final Object lock2 = new Object (); public void createDeadLock () { Thread thread1 = new Thread (() -> { synchronized (lock1) { System.out.println("Thread1 get lock1" ); try { Thread.sleep(50 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } synchronized (lock2) { System.out.println("Thread1 try get lock2." ); } } }); Thread thread2 = new Thread (() -> { synchronized (lock2) { System.out.println("Thread2 get lock2" ); try { Thread.sleep(50 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } synchronized (lock1) { System.out.println("Thread2 try get lock1." ); } } }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } public static void main (String[] args) { DeadLockSample deadLockSample = new DeadLockSample (); deadLockSample.createDeadLock(); } }
手写线程池
线程池的基本组成部分
任务队列:存储提交的任务。
工作线程:从任务队列中取出任务并执行。
线程池管理类:负责管理线程和任务的调度。
设计关键点
使用BlockingQueue存储任务。
使用Thread或Executor实现工作线程。
提供execute()方法提交任务。
管理线程的生命周期(如启动和停止线程池)。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;public class MyThreadPool { private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue; private final WorkerThread[] workers; private volatile boolean isRunning = true ; public MyThreadPool (int poolSize, int queueSize) { taskQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue <>(queueSize); workers = new WorkerThread [poolSize]; for (int i = 0 ; i < poolSize; i++) { workers[i] = new WorkerThread (); workers[i].start(); } } public void execute (Runnable task) throws InterruptedException { if (isRunning) { taskQueue.put(task); } else { throw new IllegalStateException ("ThreadPool is not running!" ); } } public void shutdown () { isRunning = false ; for (WorkerThread worker : workers) { worker.interrupt(); } } private class WorkerThread extends Thread { public void run () { while (isRunning || !taskQueue.isEmpty()) { try { Runnable task = taskQueue.poll(); if (task != null ) { task.run(); } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("WorkerThread interrupted: " + e.getMessage()); } } } } public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyThreadPool pool = new MyThreadPool (3 , 10 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 15 ; i++) { final int taskId = i; pool.execute(() -> { System.out.println("Task " + taskId + " is running on " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { Thread.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } }); } Thread.sleep(5000 ); pool.shutdown(); } }
实现生产者消费者模型 使用BlockingQueue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public class ProducerConsumerExample { private static final int BUFFER_CAPACITY = 10 ; private final BlockingQueue<Integer> buffer = new LinkedBlockingQueue <>(BUFFER_CAPACITY); public static void main (String[] args) { ProducerConsumerExample example = new ProducerConsumerExample (); new Thread (example.new Producer ()).start(); new Thread (example.new Consumer ()).start(); } class Producer implements Runnable { @Override public void run () { int value = 0 ; while (true ) { try { produce(value++); Thread.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } } private void produce (int value) throws InterruptedException { buffer.put(value); System.out.println("Produced: " + value); } } class Consumer implements Runnable { @Override public void run () { while (true ) { try { consume(); Thread.sleep(1500 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } } private void consume () throws InterruptedException { int value = buffer.take(); System.out.println("Consumed: " + value); } } }
使用wait()和notify()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 public class ProducerConsumerExample { private static final int BUFFER_CAPACITY = 10 ; private final Queue<Integer> buffer = new LinkedList <>(); private final Object lock = new Object (); public static void main (String[] args) { ProducerConsumerExample example = new ProducerConsumerExample (); new Thread (example.new Producer ()).start(); new Thread (example.new Consumer ()).start(); } class Producer implements Runnable { @Override public void run () { int value = 0 ; while (true ) { try { produce(value++); Thread.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } } private void produce (int value) throws InterruptedException { synchronized (lock) { while (buffer.size() == BUFFER_CAPACITY) { System.out.println("Buffer is full, producer is waiting..." ); lock.wait(); } buffer.add(value); System.out.println("Produced: " + value); lock.notifyAll(); } } } class Consumer implements Runnable { @Override public void run () { while (true ) { try { consume(); Thread.sleep(1500 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } } private void consume () throws InterruptedException { synchronized (lock) { while (buffer.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Buffer is empty, consumer is waiting..." ); lock.wait(); } int value = buffer.poll(); System.out.println("Consumed: " + value); lock.notifyAll(); } } } }
CompletableFuture实现异步调用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;public class AsyncExample { public static void main (String[] args) { CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(2000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "任务完成" ; }); future.thenAccept(result -> { System.out.println("异步任务结果: " + result); }); System.out.println("主线程继续执行..." ); try { String result = future.get(); System.out.println("异步任务完成后获取的结果: " + result); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
遍历HashMap 七种
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap <>(); for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue()); } for (Integer key : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(key + ":" + map.get(key)); } Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iterator.next(); System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue()); } Iterator<Integer> iterator = map.keySet().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Integer key = iterator.next(); System.out.println(key + ":" + map.get(key)); } map.forEach((key, value) -> { System.out.println(key); System.out.println(value); }); map.entrySet().stream().forEach(entry -> { System.out.println(entry.getKey()); System.out.println(entry.getValue()); }); map.entrySet().parallelStream().forEach(entry -> { System.out.println(entry.getKey()); System.out.println(entry.getValue()); });
遍历Set 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Set<Integer> row = new HashSet <>(); row.add(1 ); row.add(2 ); row.add(3 ); for (Integer number : row) { System.out.println(number); } Iterator<Integer> iterator = row.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Integer number = iterator.next(); System.out.println(number); } row.forEach(number -> System.out.println(number)); row.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
二叉树 二叉树深度 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) { val = x; left = null ; right = null ; } } public class BinaryTree { TreeNode root; public int maxDepth (TreeNode node) { if (node == null ) { return 0 ; } else { int leftDepth = maxDepth(node.left); int rightDepth = maxDepth(node.right); return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1 ; } } public static void main (String[] args) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree (); tree.root = new TreeNode (1 ); tree.root.left = new TreeNode (2 ); tree.root.right = new TreeNode (3 ); tree.root.left.left = new TreeNode (4 ); tree.root.left.right = new TreeNode (5 ); System.out.println("二叉树的深度: " + tree.maxDepth(tree.root)); } }
二叉树前序遍历转链表 二叉树的先序遍历,然后按照前序顺序将其转化为一个链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Solution { private static Node trans (TreeNode root) { Node dummy = new Node (-1 ), p = dummy; traverse(root, p); return dummy.next; } private static void traverse (TreeNode root, Node p) { if (root == null ) return ; Node node = new Node (root.val, null ); p.next = node; p = p.next; traverse(root.left, p); traverse(root.right, p); } }
有序数组转二叉平衡搜索树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) { return dfs(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); } private TreeNode dfs (int [] nums, int low, int high) { if (low > high) { return null ; } int mid = low + (high - low)/2 ; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (nums[mid]); root.left = dfs(nums, low, mid-1 ); root.right = dfs(nums, mid+1 , high); return root; } }
根据前序和中序遍历构造二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { HashMap<Integer, Integer> valToIndex = new HashMap <>(); public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) { for (int i = 0 ; i < inorder.length; i++) { valToIndex.put(inorder[i], i); } return build(preorder, 0 , preorder.length - 1 , inorder, 0 , inorder.length - 1 ); } private TreeNode build (int [] preOrder, int preStart, int preEnd, int [] inOrder, int inStart, int inEnd) { if (preStart > preEnd) { return null ; } int rootVal = preOrder[preStart]; int index = valToIndex.get(rootVal); int leftSize = index - inStart; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (rootVal); root.left = build(preOrder, preStart + 1 , preStart + leftSize, inOrder, inStart, index - 1 ); root.right = build(preOrder, preStart + leftSize + 1 , preEnd, inOrder, index + 1 , inEnd); return root; } }
根据中序和后序遍历构造二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { HashMap<Integer, Integer> valToIndex = new HashMap <>(); public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int [] postorder) { for (int i = 0 ; i < inorder.length; i++) { valToIndex.put(inorder[i], i); } return build(inorder, 0 , inorder.length - 1 , postorder, 0 , postorder.length - 1 ); } TreeNode build (int [] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, int [] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) { if (inStart > inEnd) { return null ; } int rootVal = postorder[postEnd]; int index = valToIndex.get(rootVal); int leftSize = index - inStart; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (rootVal); root.left = build(inorder, inStart, index - 1 , postorder, postStart, postStart + leftSize - 1 ); root.right = build(inorder, index + 1 , inEnd, postorder, postStart + leftSize, postEnd - 1 ); return root; } }
根据前序和后序遍历构造二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { HashMap<Integer, Integer> valToIndex = new HashMap <>(); public TreeNode constructFromPrePost (int [] preorder, int [] postorder) { for (int i = 0 ; i < postorder.length; i++) { valToIndex.put(postorder[i], i); } return build(preorder, 0 , preorder.length - 1 , postorder, 0 , postorder.length - 1 ); } TreeNode build (int [] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd, int [] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) { if (preStart > preEnd) { return null ; } if (preStart == preEnd) { return new TreeNode (preorder[preStart]); } int rootVal = preorder[preStart]; int leftRootVal = preorder[preStart + 1 ]; int index = valToIndex.get(leftRootVal); int leftSize = index - postStart + 1 ; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (rootVal); root.left = build(preorder, preStart + 1 , preStart + leftSize, postorder, postStart, index); root.right = build(preorder, preStart + leftSize + 1 , preEnd, postorder, index + 1 , postEnd - 1 ); return root; } }
迭代实现二叉树前序遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } } public class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) { return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode current = stack.pop(); result.add(current.val); if (current.right != null ) { stack.push(current.right); } if (current.left != null ) { stack.push(current.left); } } return result; } }
迭代实现二叉树中序遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) { return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); TreeNode current = root; while (current != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while (current != null ) { stack.push(current); current = current.left; } current = stack.pop(); result.add(current.val); current = current.right; } return result; }
迭代实现二叉树后续遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) { return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode current = stack.pop(); result.add(0 , current.val); if (current.left != null ) { stack.push(current.left); } if (current.right != null ) { stack.push(current.right); } } return result; }
二叉树的广度优先遍历 深度优先遍历有三种,前中后序遍历。如上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } } public class BinaryTree { public void breadthFirstTraversal (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); System.out.print(node.val + " " ); if (node.left != null ) { queue.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null ) { queue.offer(node.right); } } } public static void main (String[] args) { TreeNode root = new TreeNode (1 ); root.left = new TreeNode (2 ); root.right = new TreeNode (3 ); root.left.left = new TreeNode (4 ); root.left.right = new TreeNode (5 ); BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree (); System.out.println("Breadth-First Traversal:" ); bt.breadthFirstTraversal(root); } public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return res; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); List<Integer> level = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); level.add(node.val); if (node.left != null ) { queue.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null ) { queue.offer(node.right); } } res.add(level); } return res; } }
二叉树的最近公共祖先(LCA) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { return find(root, p.val, q.val); } TreeNode find (TreeNode root, int val1, int val2) { if (root == null ) { return null ; } if (root.val == val1 || root.val == val2) { return root; } TreeNode left = find(root.left, val1, val2); TreeNode right = find(root.right, val1, val2); if (left != null && right != null ) { return root; } return left != null ? left : right; } }
二叉树的最大路径和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { private int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE; public int maxPathSum (TreeNode root) { dfs(root); return ans; } private int dfs (TreeNode node) { if (node == null ) return 0 ; int leftVal = dfs(node.left); int rightVal = dfs(node.right); ans = Math.max(ans, leftVal + rightVal + node.val); return Math.max(Math.max(leftVal, rightVal) + node.val, 0 ); } }
二叉树最大宽度 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 class Solution { class Pair { TreeNode node; int id; public Pair ( TreeNode node, int id) { this .node = node; this .id = id; } } public int widthOfBinaryTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } int maxWidth = 0 ; Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList <>(); q.offer(new Pair (root, 1 )); while (!q.isEmpty()) { int sz = q.size(); int start = 0 , end = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; i++) { Pair cur = q.poll(); TreeNode curNode = cur.node; int curId = cur.id; if (i == 0 ) { start = curId; } if (i == sz - 1 ) { end = curId; } if (curNode.left != null ) { q.offer(new Pair (curNode.left, curId * 2 )); } if (curNode.right != null ) { q.offer(new Pair (curNode.right, curId * 2 + 1 )); } } maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, end - start + 1 ); } return maxWidth; } } class Solution2 { public int widthOfBinaryTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } traverse(root, 1 , 1 ); return maxWidth; } ArrayList<Integer> firstId = new ArrayList <>(); int maxWidth = 1 ; void traverse (TreeNode root, int id, int depth) { if (root == null ) { return ; } if (firstId.size() == depth - 1 ) { firstId.add(id); } else { maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, id - firstId.get(depth - 1 ) + 1 ); } traverse(root.left, id * 2 , depth + 1 ); traverse(root.right, id * 2 + 1 , depth + 1 ); } }
多叉树查找某个值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 class TreeNode { int value; List<TreeNode> children; public TreeNode (int value) { this .value = value; this .children = new ArrayList <>(); } public void addChild (TreeNode child) { this .children.add(child); } } public class MultiWayTree { public static boolean search (TreeNode root, int target) { if (root == null ) { return false ; } if (root.value == target) { return true ; } for (TreeNode child : root.children) { if (search(child, target)) { return true ; } } return false ; } public static void main (String[] args) { TreeNode root = new TreeNode (1 ); TreeNode child1 = new TreeNode (2 ); TreeNode child2 = new TreeNode (3 ); TreeNode child3 = new TreeNode (4 ); root.addChild(child1); root.addChild(child2); root.addChild(child3); child1.addChild(new TreeNode (5 )); child1.addChild(new TreeNode (6 )); child2.addChild(new TreeNode (7 )); child3.addChild(new TreeNode (8 )); int target = 7 ; boolean found = search(root, target); System.out.println("Found target " + target + ": " + found); } }
前缀树(Trie) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Trie { private Trie[] children; private boolean isEnd; public Trie () { children = new Trie [26 ]; isEnd = false ; } public void insert (String word) { Trie node = this ; for (int i = 0 ; i < word.length(); i++) { char ch = word.charAt(i); int index = ch - 'a' ; if (node.children[index] == null ) { node.children[index] = new Trie (); } node = node.children[index]; } node.isEnd = true ; } public boolean search (String word) { Trie node = searchPrefix(word); return node != null && node.isEnd; } public boolean startsWith (String prefix) { return searchPrefix(prefix) != null ; } private Trie searchPrefix (String prefix) { Trie node = this ; for (int i = 0 ; i < prefix.length(); i++) { char ch = prefix.charAt(i); int index = ch - 'a' ; if (node.children[index] == null ) { return null ; } node = node.children[index]; } return node; } }
图 岛屿数量 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { int [][] dirs = new int [][]{{-1 ,0 }, {1 ,0 }, {0 ,-1 }, {0 ,1 }}; public int numIslands (char [][] grid) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0 ].length; int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (grid[i][j] == '1' ) { res++; dfs(grid, i, j); } } } return res; } private void dfs (char [][] grid, int i, int j) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0 ].length; if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= m || j >= n) return ; if (grid[i][j] == '0' ) return ; grid[i][j] = '0' ; for (int [] dir : dirs) { dfs(grid, i + dir[0 ], j + dir[1 ]); } } }
二维数组搜索字符串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 public class Solution { public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int rows = board.length; int cols = board[0 ].length; for (int i = 0 ; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < cols; j++) { if (dfs(board, word, i, j, 0 )) { return true ; } } } return false ; } private boolean dfs (char [][] board, String word, int x, int y, int index) { if (index == word.length()) { return true ; } if (x < 0 || x >= board.length || y < 0 || y >= board[0 ].length || board[x][y] != word.charAt(index)) { return false ; } char temp = board[x][y]; board[x][y] = '#' ; boolean found = dfs(board, word, x + 1 , y, index + 1 ) || dfs(board, word, x - 1 , y, index + 1 ) || dfs(board, word, x, y + 1 , index + 1 ) || dfs(board, word, x, y - 1 , index + 1 ); board[x][y] = temp; return found; } }
回溯 全排列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res; public List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) { res = new LinkedList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> track = new LinkedList <>(); boolean [] used = new boolean [nums.length]; backtrack(nums, track, used); return res; } private void backtrack (int [] nums, LinkedList<Integer> track, boolean [] used) { if (track.size() == nums.length) { res.add(new LinkedList <>(track)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (used[i]) { continue ; } track.add(nums[i]); used[i] = true ; backtrack(nums, track, used); track.removeLast(); used[i] = false ; } } }
N皇后 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public class Solution { private List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) { List<String> board = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { board.add("." .repeat(n)); } backtrack(board, 0 ); return res; } private void backtrack (List<String> board, int row) { if (row == board.size()) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(board)); return ; } int n = board.get(row).length(); for (int col = 0 ; col < n; col++) { if (!isValid(board, row, col)) { continue ; } char [] rowChars = board.get(row).toCharArray(); rowChars[col] = 'Q' ; board.set(row, new String (rowChars)); backtrack(board, row + 1 ); rowChars[col] = '.' ; board.set(row, new String (rowChars)); } } private boolean isValid (List<String> board, int row, int col) { int n = board.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i <= row; i++) { if (board.get(i).charAt(col) == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i = row - 1 , j = col + 1 ; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) { if (board.get(i).charAt(j) == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i = row - 1 , j = col - 1 ; i >= 0 && j >= 0 ; i--, j--) { if (board.get(i).charAt(j) == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
数组的子集 给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。 解集不能包含重复的子集。你可以按任意顺序返回解集。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res; public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) { res = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> track = new ArrayList <>(); backtrack(nums, 0 , track); return res; } private void backtrack (int [] nums, int start, List<Integer> track) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(track)); for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) { track.add(nums[i]); backtrack(nums, i+1 , track); track.remove(track.size() - 1 ); } } }
设计模式 单例模式 单例模式确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点。
饿汉式:饿汉式单例模式在类加载时就完成实例化,线程安全,简单但可能会造成资源浪费。
懒汉式:懒汉式单例模式在第一次调用 getInstance 方法时创建实例,线程不安全,需要额外处理同步。
线程安全的懒汉式
同步方法:在 getInstance 方法上加 synchronized 关键字,保证线程安全,但是效率低。
双重检查锁定:在 getInstance 方法内部进行双重检查,保证只有第一次调用时才会加锁,提高效率。
静态内部类:利用静态内部类来实现懒加载和线程安全。
枚举:枚举实现单例模式是最简洁、安全的实现方式,可以防止反射和序列化攻击。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 public class Singleton { private static final Singleton instance = new Singleton (); private Singleton () {} public static Singleton getInstance () { return instance; } } public class Singleton { private static Singleton instance; private Singleton () {} public static Singleton getInstance () { if (instance == null ) { instance = new Singleton (); } return instance; } } public class Singleton { private static Singleton instance; private Singleton () {} public static synchronized Singleton getInstance () { if (instance == null ) { instance = new Singleton (); } return instance; } } public class Singleton { private volatile static Singleton uniqueInstance; private Singleton () { } public static Singleton getInstance () { if (uniqueInstance == null ) { synchronized (Singleton.class) { if (uniqueInstance == null ) { uniqueInstance = new Singleton (); } } } return uniqueInstance; } public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(getInstance()); } } public class Singleton { private Singleton () {} private static class SingletonHolder { private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton (); } public static Singleton getInstance () { return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE; } } public enum Singleton { INSTANCE; public void someMethod () { } public static void main (String[] args) { Singelton singleton = Singleton.INSTANCE; singleton.someMethod(); } }
工厂模式 工厂模式定义了一个用于创建对象的接口,但由子类决定实例化哪个类。它使得类的实例化延迟到子类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 interface Product { void use () ; } class ProductA implements Product { @Override public void use () { System.out.println("Using Product A" ); } } class ProductB implements Product { @Override public void use () { System.out.println("Using Product B" ); } } class ProductFactory { public static Product createProduct (String type) { if (type.equals("A" )) { return new ProductA (); } else if (type.equals("B" )) { return new ProductB (); } throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Unknown product type" ); } } public class FactoryPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { Product product = ProductFactory.createProduct("A" ); product.use(); } }
适配器模式 适配器模式将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另一个接口,使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 interface Target { void request () ; } class Adaptee { public void specificRequest () { System.out.println("Specific request" ); } } class Adapter implements Target { private Adaptee adaptee; public Adapter (Adaptee adaptee) { this .adaptee = adaptee; } @Override public void request () { adaptee.specificRequest(); } } public class AdapterPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { Adaptee adaptee = new Adaptee (); Target target = new Adapter (adaptee); target.request(); } }
装饰者模式 装饰者模式允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 interface Component { void operation () ; } class ConcreteComponent implements Component { @Override public void operation () { System.out.println("ConcreteComponent operation" ); } } abstract class Decorator implements Component { protected Component component; public Decorator (Component component) { this .component = component; } @Override public void operation () { component.operation(); } } class ConcreteDecoratorA extends Decorator { public ConcreteDecoratorA (Component component) { super (component); } @Override public void operation () { super .operation(); System.out.println("ConcreteDecoratorA additional operation" ); } } class ConcreteDecoratorB extends Decorator { public ConcreteDecoratorB (Component component) { super (component); } @Override public void operation () { super .operation(); System.out.println("ConcreteDecoratorB additional operation" ); } } public class DecoratorPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { Component component = new ConcreteComponent (); Component decoratedComponentA = new ConcreteDecoratorA (component); Component decoratedComponentB = new ConcreteDecoratorB (decoratedComponentA); decoratedComponentB.operation(); } }
策略模式 策略模式定义了一系列算法,并将每一个算法封装起来,使它们可以相互替换。策略模式使得算法可独立于使用它的客户而变化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 interface Strategy { int doOperation (int num1, int num2) ; } class OperationAdd implements Strategy { @Override public int doOperation (int num1, int num2) { return num1 + num2; } } class OperationSubtract implements Strategy { @Override public int doOperation (int num1, int num2) { return num1 - num2; } } class OperationMultiply implements Strategy { @Override public int doOperation (int num1, int num2) { return num1 * num2; } } class Context { private Strategy strategy; public Context (Strategy strategy) { this .strategy = strategy; } public int executeStrategy (int num1, int num2) { return strategy.doOperation(num1, num2); } } public class StrategyPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { Context context = new Context (new OperationAdd ()); System.out.println("10 + 5 = " + context.executeStrategy(10 , 5 )); context = new Context (new OperationSubtract ()); System.out.println("10 - 5 = " + context.executeStrategy(10 , 5 )); context = new Context (new OperationMultiply ()); System.out.println("10 * 5 = " + context.executeStrategy(10 , 5 )); } }
观察者模式 观察者模式定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,使得每当一个对象改变状态,则所有依赖于它的对象都会得到通知并被自动更新。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;interface Observer { void update (String message) ; } class ConcreteObserver implements Observer { private String name; public ConcreteObserver (String name) { this .name = name; } @Override public void update (String message) { System.out.println(name + " received: " + message); } } interface Subject { void registerObserver (Observer observer) ; void removeObserver (Observer observer) ; void notifyObservers () ; } class ConcreteSubject implements Subject { private List<Observer> observers = new ArrayList <>(); private String message; @Override public void registerObserver (Observer observer) { observers.add(observer); } @Override public void removeObserver (Observer observer) { observers.remove(observer); } @Override public void notifyObservers () { for (Observer observer : observers) { observer.update(message); } } public void setMessage (String message) { this .message = message; notifyObservers(); } } public class ObserverPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { ConcreteSubject subject = new ConcreteSubject (); Observer observer1 = new ConcreteObserver ("Observer 1" ); Observer observer2 = new ConcreteObserver ("Observer 2" ); subject.registerObserver(observer1); subject.registerObserver(observer2); subject.setMessage("Hello Observers!" ); } }
最长重复子串(不会) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 class Solution { public String longestDupSubstring (String s) { Random random = new Random (); int a1 = random.nextInt(75 ) + 26 ; int a2 = random.nextInt(75 ) + 26 ; int mod1 = random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE - 1000000007 + 1 ) + 1000000007 ; int mod2 = random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE - 1000000007 + 1 ) + 1000000007 ; int n = s.length(); int [] arr = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { arr[i] = s.charAt(i) - 'a' ; } int l = 1 , r = n - 1 ; int length = 0 , start = -1 ; while (l <= r) { int m = l + (r - l + 1 ) / 2 ; int idx = check(arr, m, a1, a2, mod1, mod2); if (idx != -1 ) { l = m + 1 ; length = m; start = idx; } else { r = m - 1 ; } } return start != -1 ? s.substring(start, start + length) : "" ; } public int check (int [] arr, int m, int a1, int a2, int mod1, int mod2) { int n = arr.length; long aL1 = pow(a1, m, mod1); long aL2 = pow(a2, m, mod2); long h1 = 0 , h2 = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; ++i) { h1 = (h1 * a1 % mod1 + arr[i]) % mod1; h2 = (h2 * a2 % mod2 + arr[i]) % mod2; if (h1 < 0 ) { h1 += mod1; } if (h2 < 0 ) { h2 += mod2; } } Set<Long> seen = new HashSet <Long>(); seen.add(h1 * mod2 + h2); for (int start = 1 ; start <= n - m; ++start) { h1 = (h1 * a1 % mod1 - arr[start - 1 ] * aL1 % mod1 + arr[start + m - 1 ]) % mod1; h2 = (h2 * a2 % mod2 - arr[start - 1 ] * aL2 % mod2 + arr[start + m - 1 ]) % mod2; if (h1 < 0 ) { h1 += mod1; } if (h2 < 0 ) { h2 += mod2; } long num = h1 * mod2 + h2; if (!seen.add(num)) { return start; } } return -1 ; } public long pow (int a, int m, int mod) { long ans = 1 ; long contribute = a; while (m > 0 ) { if (m % 2 == 1 ) { ans = ans * contribute % mod; if (ans < 0 ) { ans += mod; } } contribute = contribute * contribute % mod; if (contribute < 0 ) { contribute += mod; } m /= 2 ; } return ans; } }
A*算法 A*(A-star)算法是一种启发式搜索算法,常用于图搜索和路径规划问题。它结合了广度优先搜索和贪心最佳优先搜索的优点,使用启发式估计函数来指导搜索路径。
下面是一个简单的A*算法的Java实现,用于在二维网格上寻找从起点到终点的最短路径。假设网格中的每个节点是一个单元格,可以是可通行或不可通行的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 import java.util.*;class Node implements Comparable <Node> { public int x, y; public int g, h; public Node parent; public Node (int x, int y, int g, int h, Node parent) { this .x = x; this .y = y; this .g = g; this .h = h; this .parent = parent; } public int getF () { return g + h; } @Override public int compareTo (Node other) { return Integer.compare(this .getF(), other.getF()); } } public class AStarAlgorithm { private static final int [] DIR_X = {-1 , 1 , 0 , 0 }; private static final int [] DIR_Y = {0 , 0 , -1 , 1 }; public List<Node> aStar (int [][] grid, Node start, Node goal) { PriorityQueue<Node> openList = new PriorityQueue <>(); Set<Node> closedList = new HashSet <>(); openList.add(start); while (!openList.isEmpty()) { Node current = openList.poll(); if (current.x == goal.x && current.y == goal.y) { return constructPath(current); } closedList.add(current); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int newX = current.x + DIR_X[i]; int newY = current.y + DIR_Y[i]; if (isValid(grid, newX, newY) && !isInClosedList(closedList, newX, newY)) { int newG = current.g + 1 ; int newH = heuristic(newX, newY, goal.x, goal.y); Node neighbor = new Node (newX, newY, newG, newH, current); if (!isInOpenList(openList, neighbor)) { openList.add(neighbor); } } } } return Collections.emptyList(); } private boolean isValid (int [][] grid, int x, int y) { return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < grid.length && y < grid[0 ].length && grid[x][y] == 0 ; } private boolean isInClosedList (Set<Node> closedList, int x, int y) { return closedList.stream().anyMatch(node -> node.x == x && node.y == y); } private boolean isInOpenList (PriorityQueue<Node> openList, Node node) { return openList.stream().anyMatch(n -> n.x == node.x && n.y == node.y); } private int heuristic (int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) { return Math.abs(x1 - x2) + Math.abs(y1 - y2); } private List<Node> constructPath (Node node) { List<Node> path = new ArrayList <>(); while (node != null ) { path.add(node); node = node.parent; } Collections.reverse(path); return path; } public static void main (String[] args) { int [][] grid = { {0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, {0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }, {0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 }, {0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, {0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 } }; Node start = new Node (0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , null ); Node goal = new Node (4 , 4 , 0 , 0 , null ); AStarAlgorithm aStar = new AStarAlgorithm (); List<Node> path = aStar.aStar(grid, start, goal); for (Node node : path) { System.out.println("Node: (" + node.x + ", " + node.y + ")" ); } } }
漏桶算法 漏桶算法是一种流量整形(Traffic Shaping)和速率限制算法,用于控制数据传输速率。它通过固定容量的桶来限制数据的传输速率,当数据到达时,将数据放入桶中,然后以固定速率从桶中取出数据进行传输。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;public class LeakyBucket { private final int capacity; private final int rate; private AtomicInteger water; public LeakyBucket (int capacity, int rate) { this .capacity = capacity; this .rate = rate; this .water = new AtomicInteger (0 ); new Thread (() -> { while (true ) { try { Thread.sleep(1000 / rate); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } water.decrementAndGet(); } }).start(); } public boolean grant () { int currentWater = water.get(); if (currentWater < capacity) { water.incrementAndGet(); return true ; } return false ; } }
令牌桶算法 令牌桶算法是一种流量整形(Traffic Shaping)和速率限制算法,用于控制数据传输速率。它通过固定容量的桶来限制数据的传输速率,当数据到达时,需要获取令牌才能进行传输。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;public class TokenBucket { private final int capacity; private final int refillRate; private AtomicInteger tokens; private final long refillInterval; public TokenBucket (int capacity, int refillRate) { this .capacity = capacity; this .refillRate = refillRate; this .tokens = new AtomicInteger (capacity); this .refillInterval = 1000 / refillRate; new Thread (() -> { while (true ) { try { Thread.sleep(refillInterval); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } tokens.updateAndGet(current -> Math.min(capacity, current + 1 )); } }).start(); } public boolean grant () { int currentTokens = tokens.get(); if (currentTokens > 0 ) { tokens.decrementAndGet(); return true ; } return false ; } }
限流队列 结合漏桶算法和消息队列,实现一个限流队列,用于控制任务的执行速率。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;public class RateLimiterQueue { private final LeakyBucket rateLimiter; private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue; public RateLimiterQueue (int capacity, int rate, int queueSize) { this .rateLimiter = new LeakyBucket (capacity, rate); this .taskQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue <>(queueSize); new Thread (() -> { while (true ) { try { Runnable task = taskQueue.take(); if (rateLimiter.grant()) { new Thread (task).start(); } else { taskQueue.offer(task); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } }).start(); } public void submitTask (Runnable task) { if (!taskQueue.offer(task)) { System.out.println("任务队列已满,拒绝任务" ); } } public static void main (String[] args) { RateLimiterQueue rateLimiterQueue = new RateLimiterQueue (100 , 10 , 1000 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i++) { final int taskId = i; rateLimiterQueue.submitTask(() -> { System.out.println("处理任务:" + taskId); try { Thread.sleep(100 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } }); } } }
华为相关 课程表 你这个学期必须选修 numCourses 门课程,记为 0 到 numCourses - 1 。
在选修某些课程之前需要一些先修课程。 先修课程按数组 prerequisites 给出,其中 prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] ,表示如果要学习课程 ai 则 必须 先学习课程 bi 。
例如,先修课程对 [0, 1] 表示:想要学习课程 0 ,你需要先完成课程 1 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution { public boolean canFinish (int numCourses, int [][] prerequisites) { int [] inDegree = new int [numCourses]; List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { adjList.add(new ArrayList <>()); } for (int [] prerequisite : prerequisites) { int course = prerequisite[0 ]; int pre = prerequisite[1 ]; adjList.get(pre).add(course); inDegree[course]++; } Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { if (inDegree[i] == 0 ) { queue.offer(i); } } int [] order = new int [numCourses]; int index = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int course = queue.poll(); order[index++] = course; for (int neighbor : adjList.get(course)) { inDegree[neighbor]--; if (inDegree[neighbor] == 0 ) { queue.offer(neighbor); } } } return index == numCourses ? true : false ; } }
课程表2 现在你总共有 numCourses 门课需要选,记为 0 到 numCourses - 1。给你一个数组 prerequisites ,其中 prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] ,表示在选修课程 ai 前 必须 先选修 bi 。
例如,想要学习课程 0 ,你需要先完成课程 1 ,我们用一个匹配来表示:[0,1] 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 import java.util.*;public class CourseSchedule { public static int [] findOrder(int numCourses, int [][] prerequisites) { int [] inDegree = new int [numCourses]; List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { adjList.add(new ArrayList <>()); } for (int [] prerequisite : prerequisites) { int course = prerequisite[0 ]; int pre = prerequisite[1 ]; adjList.get(pre).add(course); inDegree[course]++; } Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { if (inDegree[i] == 0 ) { queue.offer(i); } } int [] order = new int [numCourses]; int index = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int course = queue.poll(); order[index++] = course; for (int neighbor : adjList.get(course)) { inDegree[neighbor]--; if (inDegree[neighbor] == 0 ) { queue.offer(neighbor); } } } return index == numCourses ? order : new int [0 ]; } public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int numCourses = sc.nextInt(); int m = sc.nextInt(); int [][] prerequisites = new int [m][2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { prerequisites[i][0 ] = sc.nextInt(); prerequisites[i][1 ] = sc.nextInt(); } int [] result = findOrder(numCourses, prerequisites); if (result.length == 0 ) { System.out.println("Impossible to complete all courses." ); } else { for (int course : result) { System.out.print(course + " " ); } } } }
汇总区间 JavaACM模式解题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> summaryRanges (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (nums.length == 0 ) return result; int start = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= nums.length; i++) { if (i == nums.length || nums[i] != nums[i - 1 ] + 1 ) { List<Integer> range = new ArrayList <>(); range.add(start); if (i - 1 > 0 && nums[i - 1 ] != start) { range.add(nums[i - 1 ]); } result.add(range); if (i < nums.length) start = nums[i]; } } return result; } }
合并区间 以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回 一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { int n = intervals.length; Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> { if (a[0 ] == b[0 ]) { return b[1 ] - a[1 ]; } return a[0 ] - b[0 ]; }); List<int []> res = new ArrayList <>(); res.add(intervals[0 ]); int start = intervals[0 ][0 ]; int end = intervals[0 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { int [] intv = intervals[i]; int [] last = res.get(res.size() - 1 ); if (intv[0 ] <= last[1 ]) { last[1 ] = Math.max(last[1 ], intv[1 ]); } else { res.add(intv); } } return res.toArray(new int [res.size()][]); } }
ab=c d元组个数 一个数组没有重复数字,求ab=c d的元组的个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import java.util.HashMap;public class TupleCount { public static int countTuples (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; HashMap<Integer, Integer> productMap = new HashMap <>(); int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) { int product = nums[i] * nums[j]; productMap.put(product, productMap.getOrDefault(product, 0 ) + 1 ); } } for (int k : productMap.values()) { if (k > 1 ) { count += k * (k - 1 ) / 2 ; } } return count; } public static void main (String[] args) { int [] nums = {2 , 3 , 4 , 6 }; System.out.println(countTuples(nums)); } }
轮船最小载重 给定一个货物数组int[]weight,使用轮船运往对岸,不可更改顺序,天数d,要求在d天恰好能够将货物运送完毕,请求出能在d天将货物运送完毕的轮船最小载重量。
思路:
左边界:最小载重应该是货物中最大的一项,因为一天至少需要能承载最大的货物。
右边界:最大载重应该是所有货物的总和,假如一天能运送所有货物。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class Solution { public int shipWithinDays (int [] weights, int d) { int left = 0 , right = 0 ; for (int weight : weights) { left = Math.max(left, weight); right += weight; } while (left < right) { int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; if (canShip(weights, d, mid)) { right = mid; } else { left = mid + 1 ; } } return left; } private boolean canShip (int [] weights, int d, int cap) { int daysRequired = 1 , currentWeight = 0 ; for (int weight : weights) { if (currentWeight + weight > cap) { daysRequired++; currentWeight = 0 ; } currentWeight += weight; } return daysRequired <= d; } }
将数组变锯齿数组的最小操作次数。 给一个数组int[] num,每次操作可以将数组任一元素减一,求将数组改变为锯齿状数组的最小操作数量。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class ZigzagArray { public static int minOperationsToZigzag (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int cost1 = 0 ; int cost2 = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int left = (i > 0 ) ? nums[i - 1 ] : Integer.MAX_VALUE; int right = (i < n - 1 ) ? nums[i + 1 ] : Integer.MAX_VALUE; if (i % 2 == 0 ) { int reduce = Math.max(0 , nums[i] - Math.min(left, right) + 1 ); cost1 += reduce; } else { int reduce = Math.max(0 , nums[i] - Math.min(left, right) + 1 ); cost2 += reduce; } } return Math.min(cost1, cost2); } public static void main (String[] args) { int [] nums = {9 , 6 , 1 , 6 , 2 }; System.out.println("Minimum operations: " + minOperationsToZigzag(nums)); } }
盛水最多的容器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int maxArea (int [] height) { int left = 0 , right = height.length - 1 ; int res = 0 ; while (left < right) { int cur_area = Math.min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left); res = Math.max(res, cur_area); if (height[left] < height[right]) { left++; } else { right--; } } return res; } }
装金币 有num枚金币,每枚金币的价值分别是valuei ,设置一个价值上限limitvalue,从中选一些金币出来,使金币总价值不超过limitvalue,求能选出的金币最大总和。其中value[i]和 limitvalue都是正整数。
定义状态:dp[j] 表示在总价值上限为 j 的情况下,能够选取的金币的最大总和。
状态转移方程:
选第 i 枚金币:dp[j] = dp[j]
如果选第 i 枚金币(且 j >= value[i]):dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - value[i]] + value[i])
初始化:
dp[0] = 0 表示价值上限为 0 时,选取的总价值为 0。
其余 dp[j] 初始为 0(未选任何金币时)。
目标:有金币和价值上限,计算出 dp[limitValue] 即为答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int num = sc.nextInt(); int limitValue = sc.nextInt(); int [] value = new int [num]; for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) { value[i] = sc.nextInt(); } int [] dp = new int [limitValue + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) { for (int j = limitValue; j >= value[i]; j--) { dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - value[i]] + value[i]); } } System.out.println(dp[limitValue]); } }
输入为一个数组与一个数字k,能否分组,使得每一组都刚好有k个相同的元素。思路为哈希表+取模判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import java.util.HashMap;public class Solution { public static boolean canDivideIntoGroups (int [] nums, int k) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 || k <= 0 ) { return false ; } HashMap<Integer, Integer> frequencyMap = new HashMap <>(); for (int num : nums) { frequencyMap.put(num, frequencyMap.getOrDefault(num, 0 ) + 1 ); } for (int freq : frequencyMap.values()) { if (freq % k != 0 ) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
空间复杂度O(1)判断数组是否有重复元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class DuplicateChecker { public static boolean hasDuplicate (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (nums[i] == nums[j]) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public static void main (String[] args) { int [] nums = {1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 }; System.out.println(hasDuplicate(nums)); } }
给一个二进制补码数组,求十进制数字
判断符号位:补码表示中,最高位是符号位。0 表示正数,1 表示负数。
处理正数:如果符号位是 0,直接将剩余位的二进制部分转为十进制。
处理负数:如果符号位是 1,将整个补码取反(0->1,1->0)后加 1 得到对应的绝对值,然后将其转为负数。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] binary = {1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 0 }; int decimalValue = convertToDecimal(binary); System.out.println(decimalValue); } public static int convertToDecimal (int [] binary) { int n = binary.length; boolean isNegative = binary[0 ] == 1 ; int result = 0 ; if (!isNegative) { for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { result = result * 2 + binary[i]; } } else { int [] inverted = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { inverted[i] = binary[i] == 0 ? 1 : 0 ; } int carry = 1 ; for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int sum = inverted[i] + carry; inverted[i] = sum % 2 ; carry = sum / 2 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { result = result * 2 + inverted[i]; } result = -result; } return result; } }
组合最大的时间 给6个数字,组合最大的24进制的时间。比如201456组合就是21:56:40
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class Solution { static String maxTime = "" ; public static void main (String[] args) { int [] digits = {2 , 0 , 1 , 4 , 5 , 6 }; boolean [] used = new boolean [digits.length]; dfs(digits, used, "" , 0 ); System.out.println(maxTime.isEmpty() ? "No valid time" : maxTime); } public static void dfs (int [] digits, boolean [] used, String current, int depth) { if (depth == 6 ) { String hh = current.substring(0 , 2 ); String mm = current.substring(2 , 4 ); String ss = current.substring(4 , 6 ); if (isValidTime(hh, mm, ss)) { String time = hh + ":" + mm + ":" + ss; if (maxTime.isEmpty() || time.compareTo(maxTime) > 0 ) { maxTime = time; } } return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < digits.length; i++) { if (used[i]) continue ; used[i] = true ; dfs(digits, used, current + digits[i], depth + 1 ); used[i] = false ; } } private static boolean isValidTime (String hh, String mm, String ss) { int hours = Integer.parseInt(hh); int minutes = Integer.parseInt(mm); int seconds = Integer.parseInt(ss); return hours < 24 && minutes < 60 && seconds < 60 ; } }
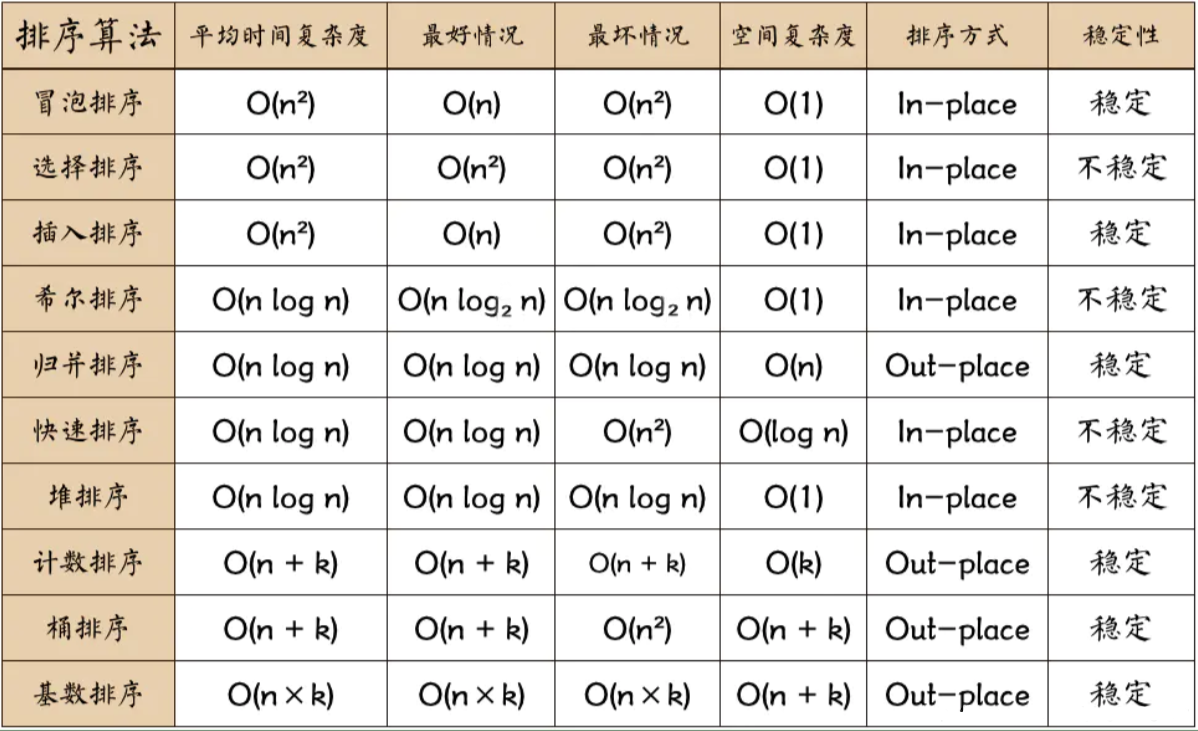
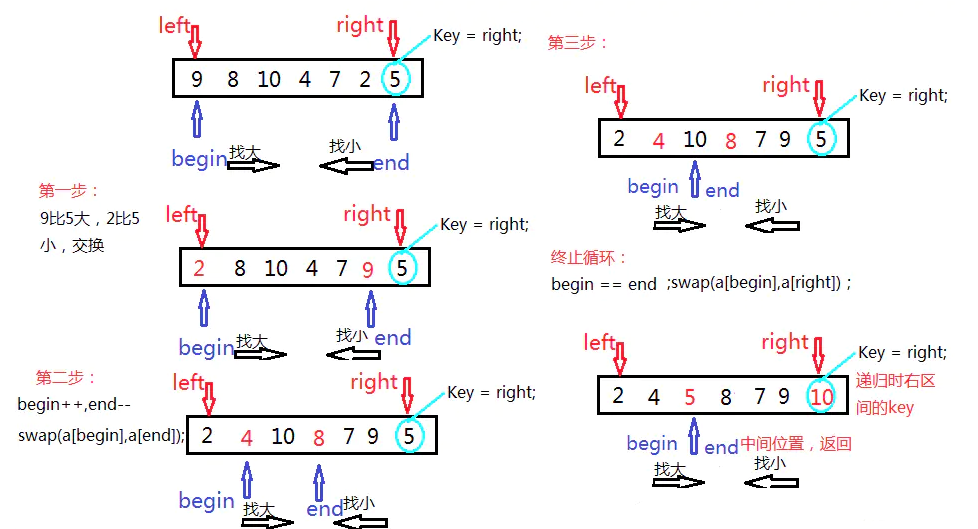 挖坑法:
挖坑法: